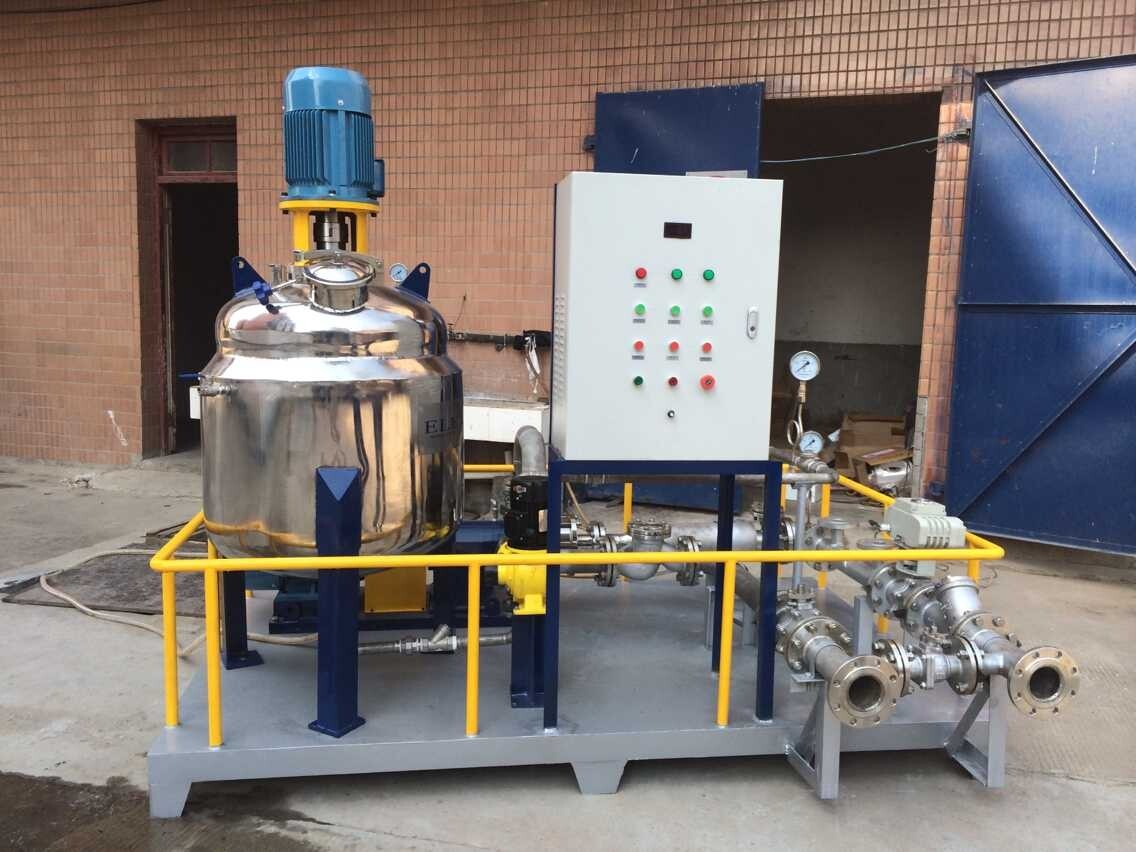
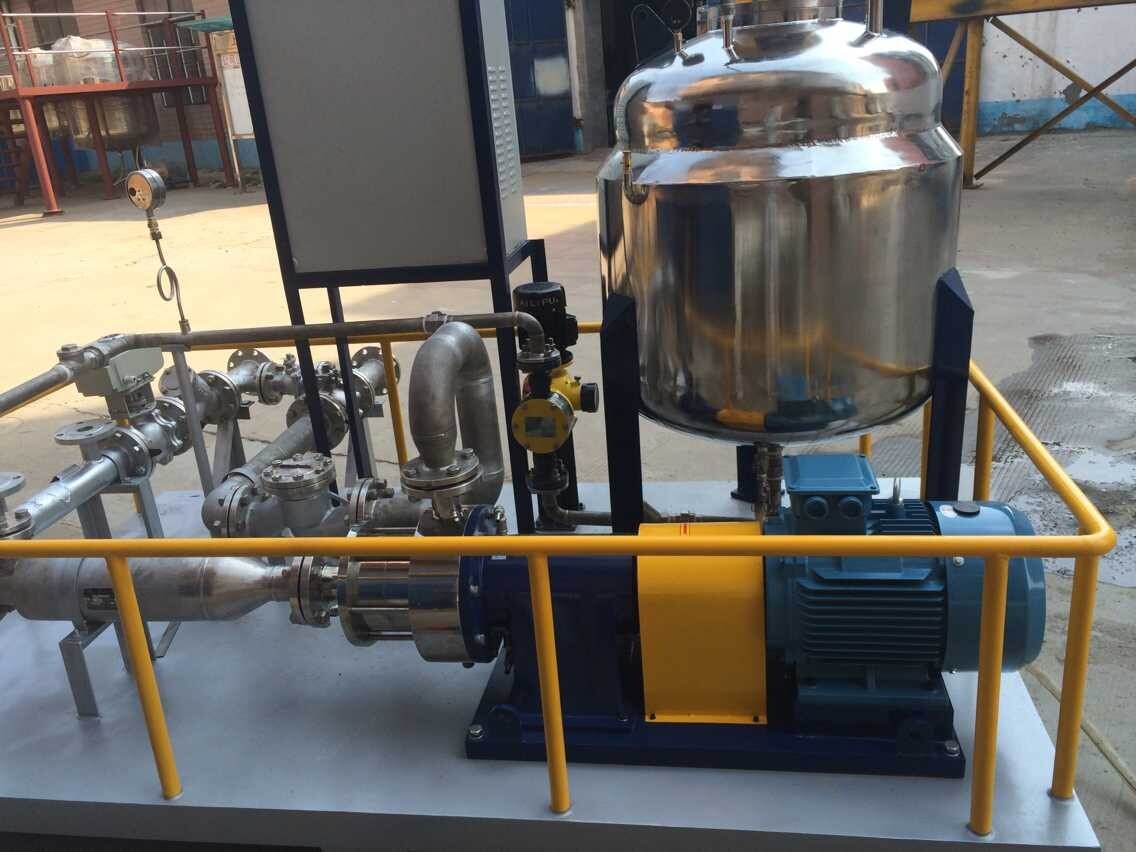
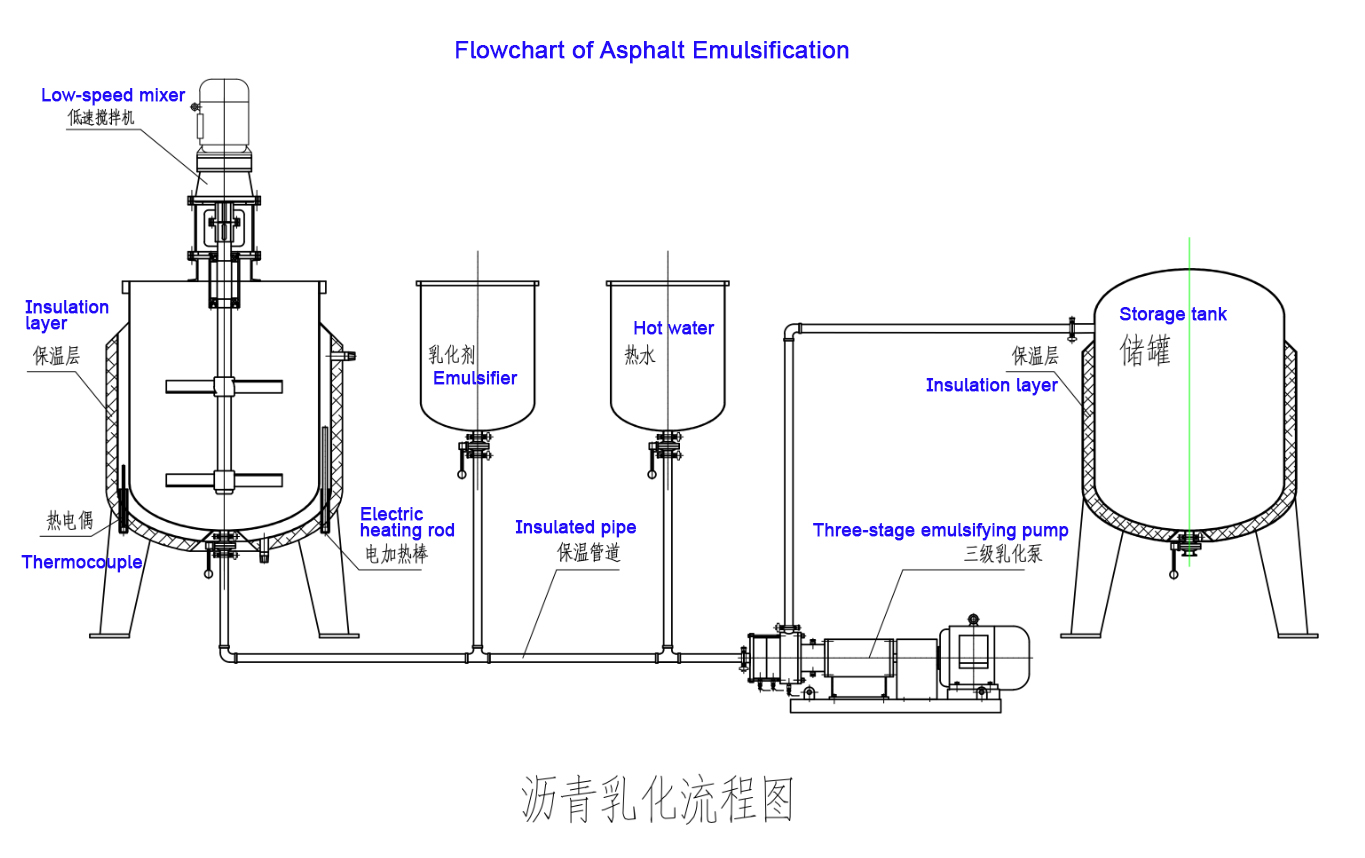
1.Emulsified asphalt production process
Depending on the production scale, various specific production conditions and process requirements, there are various forms of emulsion preparation. A typical emulsion preparation is based on water, and emulsifiers, stabilizers and additives all need to be added in the designed proportion. The process of dissolving various additives in water is carried out simultaneously. When the solution in this dissolution tank is used up, production needs to be stopped. Therefore, this is an intermittent production process, suitable for smaller-scale production. If continuous production is to be maintained, there must be more than two dissolution tanks to alternately prepare emulsifier solutions.
Various emulsifiers and stabilizers dissolve in water at different rates. To enhance the dissolution efficiency, they can be dissolved in separate tanks. For additives that are difficult to dissolve, such as PVA, the water temperature can be raised and the stirring intensity increased, and then the solution can be mixed in proportion.
Because the temperature of the emulsion used in the emulsification process is relatively low, and the dissolution of the emulsifier requires a higher water temperature to facilitate dissolution, in large-scale production equipment, the additive is dissolved first, and then the temperature is adjusted with water at a lower temperature to prepare the emulsion.
2. Modified emulsified asphalt production process
Modified emulsified asphalt refers to asphalt that is first emulsified and then modified, or both emulsification and modification processes are carried out simultaneously, resulting in an emulsified modified asphalt. Its characteristics are: The modifier adopted must be in liquid form; The production process is simple. The modifier is mixed into the emulsified asphalt in proportion and stirred, or the modifier is mixed into the emulsion in proportion to emulsify the asphalt, and thus modified emulsified asphalt is obtained.
3. Emulsified modified asphalt production process
The so-called emulsified modified asphalt is asphalt that is modified first and then emulsified. The technical routes of emulsified modified asphalt take the following three forms:
(1) Using latex as the modifier, after the asphalt is heated and melted, the latex is slowly added while stirring to evaporate the water, resulting in modified asphalt, which is then dispersed and emulsified in the prepared emulsified liquid. This form has high energy consumption and complicated procedures. The modified asphalt is difficult to disperse in the emulsion and is no longer used.
(2) Modified asphalt is made by adding solid modifiers to asphalt after solvent liquefaction and stirring, and then dispersing them in the prepared emulsion for emulsification. This form has many technological procedures, high costs, certain production risks and environmental pollution. It is rarely adopted now.
(3) Modified asphalt is made by mechanically dispersing solid thermoplastic elastomer materials with molten asphalt and then dispersing them in the prepared emulsion for emulsification. There are two major technological difficulties in this form. First, the modifier must be crushed into ultrafine particles. In emulsified modified asphalt, the particle diameter of the modified asphalt in the dispersed phase must be below 5-6 microns; otherwise, the emulsion will not be stable. Moreover, the modifier is surrounded by the asphalt components, and the particle size of the modifier must be even smaller, making it somewhat difficult to achieve high mechanical crushing. Second, it is difficult to disperse modified asphalt in emulsions. After modification, the viscosity of asphalt increases. Once mixed with the emulsion, the heat in the modified asphalt rapidly transfers to the emulsion, causing the temperature to drop rapidly and the viscosity to rise rapidly, further increasing the difficulty of highly dispersed asphalt. However, the emulsified modified asphalt produced in this way has excellent technical and economic advantages and broad application prospects.
Planar schematic diagram